Businessmen and foreign citizens, residents of other countries, taking into account the importance of the U.S. market, always wonder if the U.S. is the most important market for them.
It is possible to open a company in the United States as a foreigner.
The U.S. market is an entrepreneur’s dream. It is the most powerful market in the world and it is easier to get investment. In addition, the procedure for setting up a company is quick and easy.
Opening a branch office in the United States can be a big step for many entrepreneurs. For others, it is the opportunity to open a new business to offer products and services to millions of potential customers with high purchasing power in the world’s largest consumer market.
The great news is that it is easier to establish a business in the United States than in many other countries. The requirements are less stringent in many cases and are not require new entrepreneurs to be U.S. citizens or residents.
Some advantages of setting up a business in the United States include:
- You do not have to be a citizen or resident.
- There are many legal and highly flexible business models.
- There are no minimum capital requirements.
- There are no background checks on the founding partners.
- There is no need to appear before a notary.
- Company formation procedures are very fast and inexpensive.
- It is not necessary to come to the U.S. to advance the procedures for the creation of the company.
Becoming an entrepreneur and succeeding in the United States is not limited to these steps alone. But the company must first be created to have the opportunity to enter the market.
Creating a company in the United States requires the fulfillment of certain requirements. The following are some of the basic steps for the constitution of an foreign company in the United States.
BASIC STEPS FOR A FOREIGNER TO SET UP A BUSINESS IN THE U.S.
1 – BUSINESS PLAN: Create a Business Plan – which defines in a preliminary way, or in detail, what will be the objectives and goals of the new company.
This plan should serve as a guide for the different steps in the different stages and may be adjusted as the company and the entrepreneurs discover new circumstances and alternatives. The business plan can be useful to present to potential investment sources, partners or banks and gain their interest.
2 – MARKET RESEARCH: Use consultants and tools to make a market analysis. It is important to find out in a timely manner how it operates, what are the commercial habits, consumption habits, what is its power1, what is the competition, how costs and prices are managed, how to stand out and make your way in that market.
3 – LOCATION – CHOOSE STATE: Select the location or state in the United States in which you plan to incorporate. Considering that it is a federal country, the rules in each state are a little different. Taxes and jurisprudence on fiduciary liability differ fundamentally. Otherwise, corporate and commercial laws tend to overlap in most states. Therefore, the state where the company will be formed is definitive. That state will be the official residence of the company, but of course it will be able to do business in any of the 50 states of the United States or anywhere in the world.
For many Latin Americans, Florida is the ideal state for its location, proximity and familiarity with the Caribbean, Central and South America. In addition, it is a friendly state for foreign investors.
The state of Delaware also has some attractive features from a tax standpoint and the rules are more flexible. For this reason it is one of the favorite states to create companies that will have activities in different states and countries, and it is the preferred state for large corporations.
The Delaware court system is experienced in handling corporate litigation of all sizes, which is why it is so convenient in multinational negotiations.
4 – NAME: Select the unique name of the company and verify its availability for registration. The name is an important beginning that reflects the purpose of the company. It is also convenient that there is an equivalent or similar domain for the Internet.
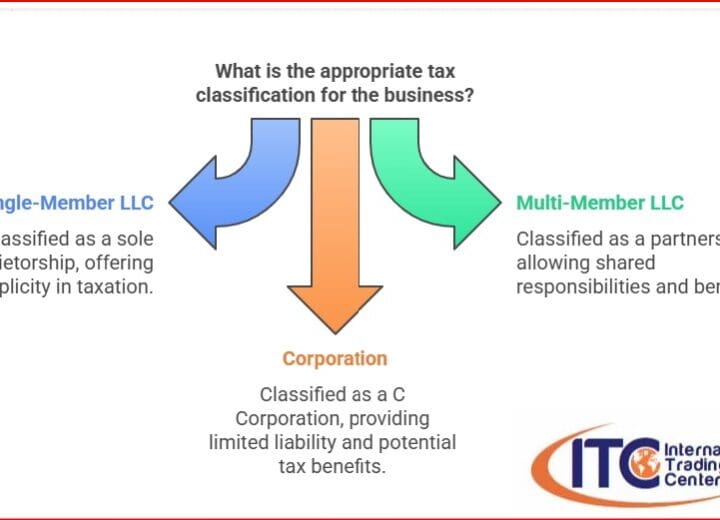
5 – STRUCTURE OF THE COMPANY: Determinewhat kind of company it will be. There are several options. The most common for this case are the Corporation, or the LLC – Limited Liability Company. There are different legal figures with their specific characteristics and in order to select the most appropriate one, the following must be considered
consider your business model, the number of partners, how they provide start-up capital, etc.
The main corporate structures to create a company are:
A) Sole Proprietorship: It is the simplest and cheapest structure and does not demand many requirements, which is its main advantage. The owner has unlimited liability. The disadvantage is that if the company has losses, the owner is personally liable for these debts. It is not the one we recommend to foreign entrepreneurs, who must also have their immigration status defined.
B) Corporation: These are entities independent of their owners. Shareholders are only liable for what they have invested in the company.
There are two types of corporations (Class “S” and “C”) and they are differentiated by the tax obligations to which they are subject.
Class S is recommended for a single owner and Class C when there are several partners and potential investors.
S Corporation: In this case there is no double taxation, the partners have limited liability. It is a structure whose formation is more expensive and complex than the LLC but with advantages similar to those of a CCL and some advantages of the Corporation. The member must be a U.S. resident citizen.
The C Corporation is also a good option, especially if there are several partners and potential investors. Expansion is possible by offering limited shares and are more attractive to investors, although profits must be taxed twice.
Corporate shareholders have advantages because they qualify for a lower dividend rate.
Although there is double taxation, corporate and partner taxation, tax management strategies allow for some options that increase expenses, reduce profits and consequently reduce some of the double taxation.
C) Limited Liability Company LLC (Limited Liability Company): This is the most flexible business structure. Thus, it is presented as a combination of a corporation and a limited partnership. The LLC is one of the most attractive business structure options for a start-up company of a foreign entrepreneur.
In the case of the LLC, it can be managed by one or more members. The owners of the LLC are known as members, and are not personally liable for the obligations of the company.
The company’s profits are transferred to the members, who incorporate this income into their personal income for their individual tax returns.
D) Partnerships: They are formed by two or more persons or entities that own and manage the company. The partners share profits, losses and management. In addition, taxes are the individual responsibility of the partners.
6 – PHYSICAL ADDRESS: A physical business address is required to create a Corporation or LLC, and a Registered Agent must also have a local address. The Registered Agent is the official contact for the receipt of the company’s legal documents (subpoenas, garnishments, lawsuits, etc.). Most companies do not start with their own office and therefore contract services with Business Centers (such as the International Trading Center-ITC).
7 – INCORPORATION: With the above points clear and defined, the company must submit its application for incorporation to the Department of State, or the Division of Corporations of the respective State. For the incorporation form the corporation must have: defined the name of the corporation, the selected structure, the physical address, name and address of the registered agent, the par value of the shares authorized to be issued by the corporation, who are its members and officers, and pay the respective state incorporation fee.
8 – TAXES: It is essential to obtain an identification for the IRS (Internal Revenue Service), that is to say, a tax number. The company is required to obtain an EIN (Employer Identification Number), a social security number (only if they are residents) or an ITIN (in their personal capacity), to proceed with opening bank accounts, hiring employees and of course, complying with IRS requirements.
9 – AN ACCOUNTANT: In order to comply with tax regulations and meet tax obligations in a timely manner, an accountant, a CPA (Certified Public Accountant), must be hired. This advisor prepares annual tax returns and advises the company on tax issues, sales tax returns, and other requirements that may arise depending on the business. All companies pay federal income tax; U.S. resident companies must pay state income tax in their state of residence. State and local governments may impose taxes on income.
10 – LICENSES: Request and process the different licenses and permits required. These are sometimes required by the city, county or state and generally depend on the type of business it is. For these initial procedures, it is advisable to seek the advice of someone who is familiar with these procedures in order to comply on time and avoid incurring in faults that could lead to fines.
11 – IMMIGRATION: The company may be incorporated by foreigners. But in the future development of the business, in the management of the business and in the projections of the business, it is necessary to consider whether or not there are plans to immigrate to the United States, if someone needs to come and manage the company, etc. For these purposes, it is necessary from the beginning to seek the advice of an immigration lawyer, who will be able to inform you of the numerous options and types of visas that exist for entrepreneurs and investors. There are numerous business visa options and each has specific requirements and is facilitated for certain businesses. This is an important issue that is best known from the beginning, even if the needs do not present themselves until gradually.
12 – BANK ACCOUNT: Commercial bank accounts help with the management of the company on several levels and are a reflection of seriousness in business. Banks often offer some services or benefits that are not offered in personal accounts. Not all banks are equally interested in promoting and supporting the creation of new companies with foreign partners.